(Troubleshooting) Hibernate MultipleBagFetchException 정복하기

Trouble
Spring Data JPA를 이용하다보면 종종 org.hibernate.loader.MultipleBagFetchException: cannot simultaneously fetch multiple bags이란 메세지를 보게 된다.
우선 어떤 상황에 나타나는지 한 번 살펴보자.1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
public class Mother {
private Long id;
private List<Daughter> daughters = new ArrayList<>();
private List<Son> sons = new ArrayList<>();
public Mother(final Long id, final List<Daughter> daughters, final List<Son> sons) {
this.id = id;
if(daughters == null) this.daughters = new ArrayList<>();
else {
daughters.forEach(daughter -> daughter.setMother(this));
this.daughters = daughters;
}
if(sons == null) this.sons = new ArrayList<>();
else {
sons.forEach(son -> son.setMother(this));
this.sons = sons;
}
}
public void bearDaughters(final List<Daughter> babyDaughters) {
babyDaughters.forEach(daughter -> daughter.setMother(this));
daughters.addAll(babyDaughters);
}
public void bearSons(final List<Son> babySons) {
babySons.forEach(son -> son.setMother(this));
sons.addAll(babySons);
}
}
엄마가 있고, 아들/딸들이 있는데 아들/딸들을 EAGER로 fetch해 올 때 발생한다.
(즉, OneToMany, ManyToMany인 Bag 두 개 이상을 EAGER로 fetch할 때 발생한다.)
EAGER로 땡겨오면 N+1 쿼리 문제가 존재하기 때문에 fetchType을 전부 LAZY로 바꾼 후 한 방 쿼리로 불러와도 문제는 재발한다.1
2
3
4public interface MotherRepository extends JpaRepository<Mother, Long> {
List<Mother> findAllWithChildrenBy();
}
Bag
우선 MultipleBagFetchException 파일을 둘러보자.1
2
3
4/**
* Exception used to indicate that a query is attempting to simultaneously fetch multiple
* {@link org.hibernate.type.BagType bags}
*/
여러 BagType을 동시에 fetch 해 올 때 발생하는 예외라고 한다.
그럼 Bag이 뭘까…?
A generalization of the notion of a set is that of a multiset or bag, which is similar to a set but allows repeated (“equal”) values (duplicates).
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Set_(abstract_data_type)#Multiset
A Bag is a java collection that stores elements without caring about the sequencing, but allow duplicate elements in the list.
A bag is a random grouping of the objects in the list.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Set_(abstract_data_type)#Multiset
A
is an unordered collection, which can contain duplicated elements.
That means if you persist a bag with some order of elements, you cannot expect the same order retains when the collection is retrieved.
There is not a “bag” concept in Java collections framework, so we just use a java.util.List corresponds to a.
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/13812283/difference-between-set-and-bag-in-hibernate
즉, Bag(Multiset)은 Set과 같이 순서가 없고, List와 같이 중복을 허용하는 자료구조이다.
하지만 자바 컬렉션 프레임워크에서는 Bag이 없기 때문에 하이버네이트에서는 List를 Bag으로써 사용하고 있는 것이다.
Troubleshooting
우선 두 Bag을 Set으로 바꾸면 우리가 원하는대로 한 방 쿼리로 날아간다.1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
public class Mother {
private Long id;
private Set<Daughter> daughters = new HashSet<>();
private Set<Son> sons = new HashSet<>();
public Mother(final Long id, final Set<Daughter> daughters, final Set<Son> sons) {
this.id = id;
if(daughters == null) this.daughters = new HashSet<>();
else {
daughters.forEach(daughter -> daughter.setMother(this));
this.daughters = daughters;
}
if(sons == null) this.sons = new HashSet<>();
else {
sons.forEach(son -> son.setMother(this));
this.sons = sons;
}
}
public void bearDaughters(final Set<Daughter> babyDaughters) {
babyDaughters.forEach(daughter -> daughter.setMother(this));
daughters.addAll(babyDaughters);
}
public void bearSons(final Set<Son> babySons) {
babySons.forEach(son -> son.setMother(this));
sons.addAll(babySons);
}
}
실무에서 급하면 딱 이 수준까지만 하면 끝이고 이제 왜 Multiple Bag을 Fetch해 올 수 없는지 알아보자.
우선 두 Bag 중 하나만 Set으로 바꾼 후 결과를 보자.1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
public class Mother {
private Long id;
private Set<Daughter> daughters = new HashSet<>();
private List<Son> sons = new ArrayList<>();
public Mother(final Long id, final Set<Daughter> daughters, final List<Son> sons) {
this.id = id;
if(daughters == null) this.daughters = new HashSet<>();
else {
daughters.forEach(daughter -> daughter.setMother(this));
this.daughters = daughters;
}
if(sons == null) this.sons = new ArrayList<>();
else {
sons.forEach(son -> son.setMother(this));
this.sons = sons;
}
}
public void bearDaughters(final Set<Daughter> babyDaughters) {
babyDaughters.forEach(daughter -> daughter.setMother(this));
daughters.addAll(babyDaughters);
}
public void bearSons(final List<Son> babySons) {
babySons.forEach(son -> son.setMother(this));
sons.addAll(babySons);
}
}
그리고 MotherRepository#findAllWithChildrenBy() 메서드를 통해 호출하면 아래와 같은 결과를 볼 수 있다.
일단 날아간 쿼리는 아래와 같다. (혹시나 join 했을 때 자식들이 없을까봐 엄마라도 불러오려고 기본적으로 outer join을 하고 있다.)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18select
mother0_.id as id1_1_0_,
daughters1_.id as id1_0_1_,
sons2_.id as id1_2_2_,
daughters1_.mother_id as mother_i2_0_1_,
daughters1_.mother_id as mother_i2_0_0__,
daughters1_.id as id1_0_0__,
sons2_.mother_id as mother_i2_2_2_,
sons2_.mother_id as mother_i2_2_1__,
sons2_.id as id1_2_1__
from
mother mother0_
left outer join
daughter daughters1_
on mother0_.id=daughters1_.mother_id
left outer join
son sons2_
on mother0_.id=sons2_.mother_id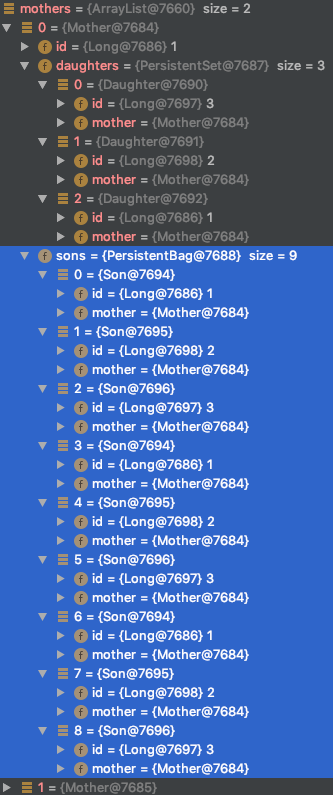
Set으로 저장한 딸들은 중복없이 잘 불러와졌고, List(Bag)로 저장한 아들들은 중복있이 잘 불러와졌다.
(List라고 무조건 중복이 발생하는 건 아니다. 단일 List(Bag)만 Fetch 해오면 중복없이 잘 불러온다.)
이 결과를 Row로 표시해보자면 다음과 같다.
| mother.id | daughter.id | son.id |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 2 |
| 1 | 1 | 3 |
| 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 1 | 3 | 1 |
| 1 | 3 | 2 |
| 1 | 3 | 3 |
만약 daughters 마저도 중복도 보장이 안 되고, 순서도 보장이 안 됐다면 어떤 기준을 가지고 Row를 매핑할 수 있을까?
(뭐, 물론 이 경우에는 될 수도 있겠지만 좀 더 엔터티의 관계가 복잡한 경우에는 매핑이 불가능하거나 너무 복잡해지는 거 아닐까?)
그렇기 때문에 Multiple Bag은 Fetch가 안 되는 게 아닐까 싶다.
실제로 List로 저장한 데이터를 하이버네이트에서는 BagType으로 취급하고 있고, Set으로 저장한 데이터는 SetType으로 취급하고 있다.
ListType 클래스도 있긴 한데 언제 어떻게 써야하는지는 잘 모르겠다 ㅠㅠ…